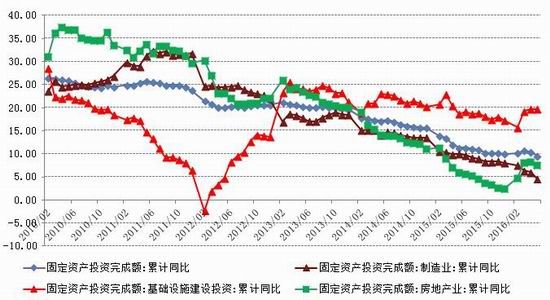
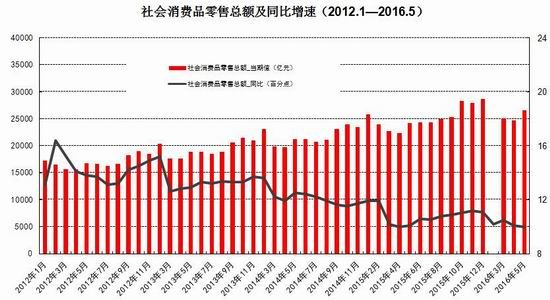
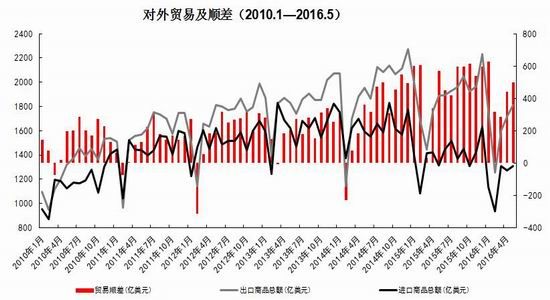
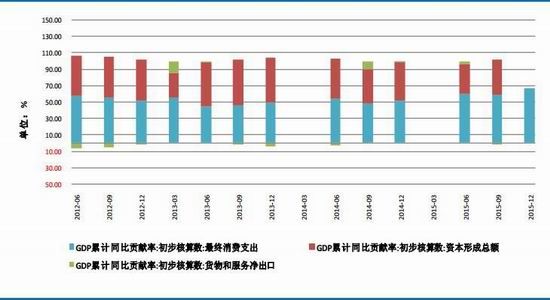
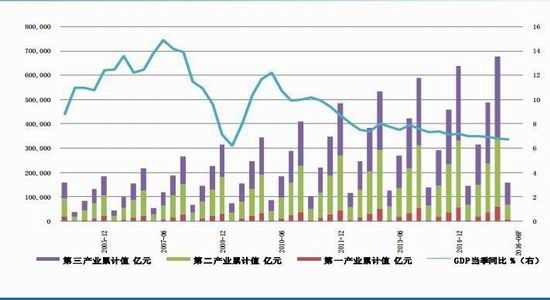
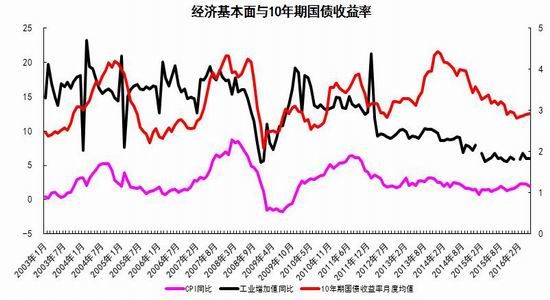
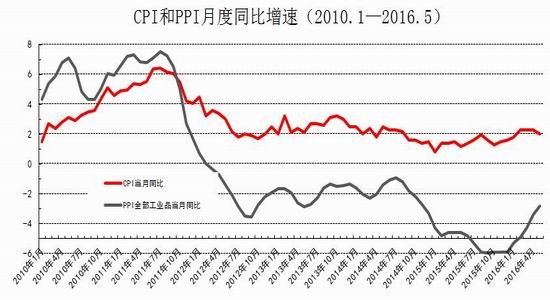
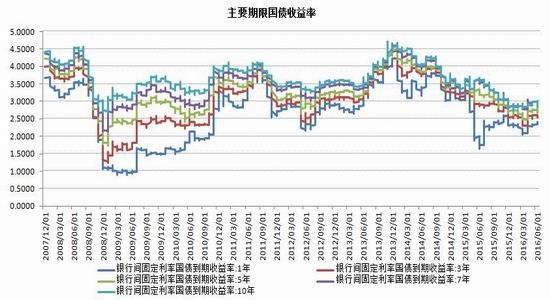
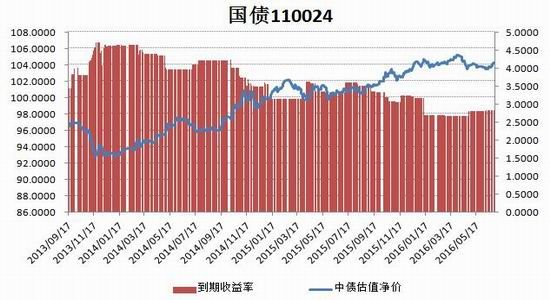
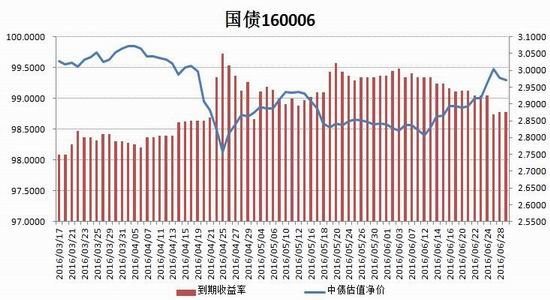
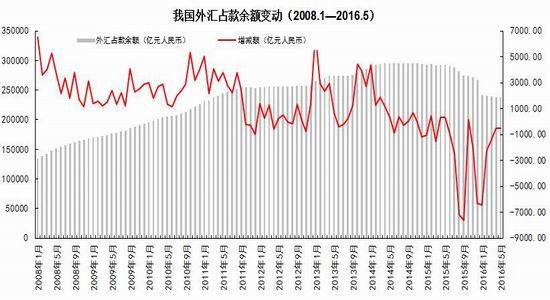
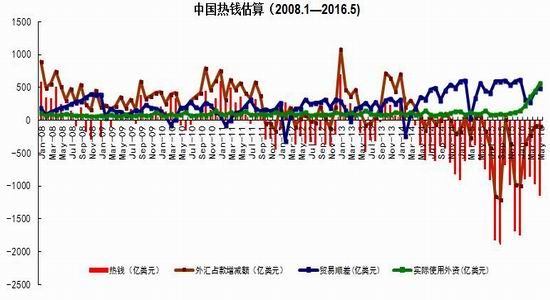
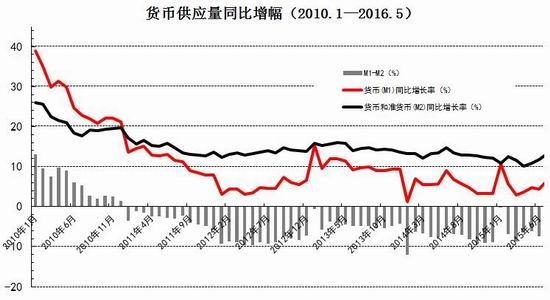
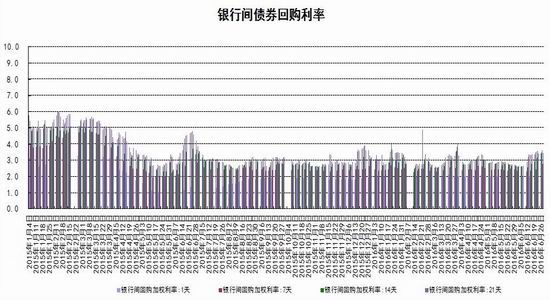
From the perspective of the impact of monetary policy and fiscal policy, inflation expectations are superimposed on the pressure of RMB depreciation, the monetary policy operation space is further reduced, the central bank's monetary policy is prudent and cautious, coupled with the pressure on the supply of interest rate bonds, the short-term yield is stable and long. The downside of bond yields is limited. It is expected that the yields of five bonds and ten bonds will fluctuate between 2.30-2.70% and 2.80-3.10% in the second half of the year, and the debt operation will be dominated by shocks. The first part of the fundamental and financial analysis I. China's economy 1. The economy is weak and stable 1.1 Investment growth slows down, infrastructure bottoming In terms of investment, although the growth rate of investment has slowed down, the investment structure continues to be optimized. In the first five months of 2016, the national fixed asset investment (excluding farmers) was 1,877.1 billion yuan, an increase of 1.6 trillion yuan over the same period of last year, a nominal increase of 9.6% year-on-year, and the growth rate dropped by 0.9 percentage points from the first four months. Among them, tertiary industry investment and infrastructure investment increased by 11.9% and 20% respectively. From the perspective of the three major sectors, only the infrastructure investment performed well, and the growth rate of real estate development and manufacturing investment both lowered the growth rate of investment in the current period. From January to May, the growth rate of private fixed assets investment reached a record low, up 3.9% year-on-year. Due to the overcapacity adjustment in the upstream industry, the growth rate of investment in some industries dropped significantly. Year-on-year growth rate of fixed assets investment completion (2010.2—2016.5) Figure 1> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute In May, the growth rate of fixed-asset investment in the month was only 9.6%, and the fall rate exceeded expectations. The main component of the manufacturing industry fell sharply. The cumulative investment in May increased by 4.6%, and the growth rate dropped by 1.4 percentage points from the previous month. It grew by 19.75%, up 0.2 percentage points from the previous month and slightly higher than 19.3% in the first quarter. Benefiting from loose monetary policy and other policy support, infrastructure investment continues to maintain a relatively fast growth. At the same time, however, considering that the contradiction between fiscal revenue and expenditure has not been alleviated, the rate of return on infrastructure investment is gradually declining, and high-speed growth may not be maintained for a long time. In terms of real estate, the cumulative growth rate of investment fell by 0.2 percentage points to 7%. The time required for the current round of sales to be transmitted to the investment terminal is longer, indicating that real estate companies are becoming more cautious in the context of high economic growth and high commodity housing stocks. In addition, some hot cities have successively introduced land control policies, which are also conducive to market return. reason. Since June, with the relatively stable saleable area, the sales of commercial housing in 30 large and medium-sized cities have undergone major adjustments, which may have certain impact on the growth of the sales and real estate industry. Once the future sales continue to adjust, real estate investment Or will continue to be under pressure. In the future, the demand for the real economy is still relatively low, and most traditional industries still face huge pressures of overcapacity. Affected by this, it is expected that traditional industrial and manufacturing investment will continue to slow down, which will further reduce the overall growth rate of fixed investment. 1.2 Consumption growth slows down In terms of consumption, the consumer market performed relatively well, but the risk is still relatively large. From January to May 2016, the total retail sales of consumer goods was 1,292.8 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10.2%. Among them, the retail sales of consumer goods above designated size was 580 billion yuan, an increase of 7.4%. In May, the total retail sales of consumer goods reached 266.11 billion yuan, a nominal increase of 10.0% year-on-year. Among them, the retail sales of consumer goods above designated size was 1,188.5 billion yuan, an increase of 6.5%. According to the data in May, in addition to the three categories of commodities such as automobiles, Chinese and Western medicines and daily necessities, the growth rate of consumption of other commodities has declined to varying degrees, especially household appliances and audio equipment. The growth rate was 8.4 percentage points lower than that in April. In addition, the growth rate of construction and decoration consumption also dropped by 0.5 percentage points from the previous month, which does not match the recent sales data of the property market. Generally speaking, under the spur of real estate sales, the home appliance and building decoration market will also perform well. For the current data trend, we need to be alert to the risk of a real estate bubble. The year-on-year growth rate of total retail sales of social consumer goods (2010.1—2016.5) Figure 2> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute Overall, the deterioration of business prospects, the slowdown in salary growth, and the decline in consumer confidence have affected residents' consumption performance. After experiencing a short-term rebound in government stimulus policies, car sales once again returned to weak growth, and the growth rate of retail sales of household appliances, video equipment and communications continued to slow down. With the weakening of consumer sales in the later period, the combination of the economy will continue to decline, and the growth rate of consumption in the later period may fall slightly. 1.3 Import and export continue to be under pressure According to customs statistics, in the first five months, China’s total import and export value was 9.16 trillion yuan, down 3.2% from the same period last year. Among them, exports were 5.28 trillion yuan, down 1.8%, narrowing by 0.9 percentage points; imports were 3.88 trillion yuan, down 5%, narrowing by 2.5 percentage points; trade surplus was 1.4 trillion yuan, an increase of 8.2%. Foreign trade balance Figure 3> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute In the month of May, China’s total import and export value was 2.02 trillion yuan, an increase of 2.8%. Among them, exports were 1.17 trillion yuan, up 1.2%, for three consecutive months; imports were 847.1 billion yuan, up 5.1%, ending 18 months of continuous decline; trade surplus was 324.8 billion yuan, narrowing 7.7%. In May, exports were lower than April, which was due to external demand. In May, the US, Eurozone, and Japanese manufacturing PMIs were down 0.1, 0.2, and 0.5 respectively. The collective weakness of the prosperity index indicates that external demand growth is still limited; Exports in April last year were weaker than in May, and the base effect was also dragged down by exports in May. The export situation has continued to weaken since it rebounded sharply in March this year. It also reflects the continued downturn in the external economy. The demand has not been fundamentally improved, and the future export situation is still grim. In addition, from the perspective of the exchange rate, in the context of the weak global economy, the depreciation of the RMB since the beginning of the year has not significantly improved exports. With the decision of the British referendum to leave the European Union and the US economy to be less than expected, the Fed’s interest rate hike is expected to be pushed back again. We believe that the pressure of RMB depreciation will improve in the future and the promotion of exports will be limited. In terms of imports, the month of imports in May was significantly better than the previous period, and the cumulative value in January-May was -0.5%. Since the beginning of the year, commodity prices, infrastructure and real estate growth have been good, and upstream companies have replenished their stocks. These factors have jointly promoted the continuous improvement of import data. At the same time, however, capital investment has shown a downward trend, and it is difficult for domestic demand to have further room for recovery in the future. Overall, from the import and export data of the first five months, the foreign trade situation has not improved fundamentally. For the first time this year, the government has not set a target for foreign trade growth. It also reflects that the prospects for foreign trade are unclear, and it is difficult to expect to drive the economy through exports. On the whole, the external economy is trending and the external demand is weak, which makes the export continue to be weak. In May, China’s foreign trade export leading index was 33.1, down 0.7 from last month. It also indicates that exports in the third quarter are facing further downward pressure. On the import side, combined with the price and price, the weakness of this year's imports will continue, but the contraction will be moderated under the effect of low base. We believe that the margin of foreign trade will be better in the second half of this year, but it is unlikely that there will be a clear recovery. 1.4 China's economic elasticity increases In the first quarter of 2016, the GDP was 1,582.6 billion yuan, calculated at comparable prices, up 6.7% year-on-year, down 0.1 percentage points from the fourth quarter of last year. In 2015, the GDP growth in the first quarter of this year was 95.51 billion yuan. In the same period of last year, it increased by 22.2 billion yuan. Contribution rate of China's three major needs to GDP growth (2011.1Q—2016.1Q) Figure 4> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute In the first quarter, the demand structure was further improved. The contribution rate of final consumption expenditure to GDP growth was 66.4%, an increase of 15.4 percentage points over the previous year. At the same time, energy conservation and consumption reduction have continued to make new progress. The annual energy consumption per unit of GDP has decreased by 5.6% compared with the previous year. Adding blocks to the development of the service industry and increasing the proportion of the service industry in the tertiary industry structure will help alleviate the shortage of energy resources and improve the efficiency of resource utilization. It will also help to promote economic restructuring and accelerate the transformation of economic development. China's quarterly GDP (2011.1Q—2016.1Q) Figure 5> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute In the context of the Chinese economy entering a new normal, there have been some changes in both the growth structure and the growth rate. In terms of industries, the added value of the primary industry was 880.3 billion yuan, up 2.9% year-on-year; the added value of the secondary industry was 595 billion yuan, up 5.8%; the added value of the tertiary industry was 90.214 billion yuan, up 7.6%. Under the policy support and structural adjustment, the primary industry increased slightly year-on-year, but the growth rate slowed down; the secondary industry was affected by the adjustment and upgrading of the industrial structure, and the growth rate continued to decline; the growth rate of the tertiary industry declined slightly, but Still higher than GDP growth rate, the contribution rate to GDP reached 62.8%, which has become an important pillar of the national economy. At the same time, China's GDP growth rate is still showing a downward trend. In the context of the global economic downturn, domestic and foreign demand is weak, and the downward pressure on economic production is not diminished by the supply-side reform and restructuring. Despite the recent signs of short-term stabilization, it can be seen from the data that the economic recovery is not stable and is still in the process of repeatedly bottoming out. 2. The inflationary pressure is weakened Inflation and economic growth are fundamental factors that determine the direction of Treasury yields and price movements. China's inflation, economic growth and government bond yields Figure 6> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute From the long-term relationship between economic growth, inflation and bond yields, inflation has a strong direct correlation with the yield of government bonds, and economic growth also determines the direction of the change in the yield of government bonds. In terms of industrial growth, in the first half of this year, the growth rate of industrial enterprises above designated size showed a bottoming out. In the first two months of this year, the added value of industrial enterprises above designated size increased by 5.4% year-on-year, the lowest level since November 2008, followed by easing policy. Under the favorable environment of overweight and steady growth policies, the industrial growth rate has rebounded. The value added of industrial enterprises above designated size increased by 5.9% year-on-year in the first five months. At the same time, the policy level will continue to set the tone for the “structural adjustment is the main line†throughout the year, and the industrial growth rate in the second half of the year may decline slightly. In the short-term, supply-side reform will continue to slow down the growth rate of upstream industries, but in the medium and long term, selective elimination is the only way to maintain industrial competitiveness. Cpi and ppi Figure 7> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute In the first five months of 2016, the national consumer price level rose by 2.1% over the same period of last year, and the core CPI was 1.6%. In May, the monthly CPI rose by 2.0% year-on-year, down 0.5% from the previous month. It is undeniable that the level of CPI in 2016 is slightly higher than that in 2015. The upward trend of wage level and land rent level has also raised the CPI level to some extent. However, on the basis of economic stability and the decline of private investment, the growth rate of M2 has remained stable. There is no basis for the CPI to rise substantially, but a steady upward trend has taken shape. Based on the existing static tail, it is estimated that the annual CPI for 2016 will be about 2%. Since the first half of the year, the central bank has adopted a RRR cut and multiple MLF operations in a disguised form, keeping monetary policy slightly loose on a sound basis, and liquidity release has raised the effect on prices. However, the current policy has gradually turned to a stable state, the capital fabric will be tightened slightly, the monetary policy will not release a large amount of liquidity, and the effect of raising prices will be difficult to sustain. The upward pressure of CPI will decrease in the second half of the year, and the restrictions on monetary policy will also be weakened. In May, the PPI fell by 2.8% year-on-year, and it has been negative for 51 consecutive months, but the decline was 0.6 percentage points lower than the previous month, narrowing for the fifth consecutive month. Under the influence of the improvement of downstream demand, the stabilization of the price of upstream production materials and the decline of the base, the decline in the ex-factory price of industrial products has narrowed to -2.8% for five consecutive months. On the one hand, due to the low price of industrial products in 2015, the price has bottomed out, leading to a higher probability and space for the price rebound in the first half of this year. On the other hand, the price of the upstream mining industry continues to rise, driving the price of industrial products to rebound. Among them, the prices of oil and natural gas exploration and petroleum processing industries increased by 12.3% and 4.1% respectively, while the prices of coal mining and washing industry also rebounded from the previous month. In addition, since the beginning of the year, the economic operation has shown signs of short-term improvement. The growth rate of fixed-asset investment is 0.5 percentage points higher than that at the end of last year. The growth rate of real estate development investment has increased significantly. A large number of infrastructure projects have started, and the downstream market demand has improved significantly, which has also driven the PPI trend. Better. For the future trend of industrial product prices, due to the low base effect, the PPI year-on-year decline should continue to narrow. At the same time, as the price of bulk commodities has come to an end, and China's industrial clearing has not yet been completed, domestic inventories have begun to rise, and the future PPI continues to rebound, and there is still a downside. Second, the international macro In the first half of 2016, the global economy continued its low-speed recovery. The bottoming out of energy prices helped the inflation level rebound slightly. The UK's “Brexit†referendum and the Fed's delayed interest rate hike were the focus of the market in the first half of the year. The US election, the Middle East and the Korean Peninsula Geopolitical risks have brought many destabilizing factors to the economy. In terms of regions and countries, developed economies such as the United States, the Eurozone, and Japan are weak in growth. India maintains a high-speed growth momentum, and other emerging markets and developing economies are facing different levels of downward pressure. The global economic growth is weak and there are many potential risks. The IMF and the World Bank have twice lowered their global economic growth forecasts this year. Looking forward to the second half of the year, the acceleration of manufacturing expansion and the continued recovery of the real estate industry will boost the economic growth of the United States in the second half of the year. However, there are certain hidden dangers in the employment market. The cautious behavior of the Fed’s delay in raising interest rates will make the US dollar index unable to break the turbulent situation. The level is expected to continue to rise. The economic prospects of the Eurozone are slightly dim. The Brexit will damage the economy and frustrate the market confidence. The loose monetary environment will continue to be maintained. To boost the economy, the European Central Bank may have more easing in the year. Japan's economic growth is weak, and it will continue to face problems such as slow salary growth, appreciation of the yen, and sluggish domestic and international demand. It will force the Japanese government to increase fiscal stimulus and monetary stimulus. However, the Bank of Japan has limited options for loose tools and its effects are worrisome. The Fed’s interest rate hike, the Brexit negotiations and the US presidential election will be hot topics in the international macro economy in the second half of 2016. The Fed is expected to raise interest rates most in December, with the US dollar index fluctuating between 93 and 97. The Brexit negotiations in the UK are highly uncertain and need to be closely watched. The US presidential election will affect US economic policies and thus the price of financial assets. Third, the current coupon analysis In the second quarter, the yield curve was slightly higher than that in the first quarter, and it was flattened. The short-end increase was higher than the mid-end. Main term bond yields Figure 8> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute From the monthly average, the yield of the main term bond in June was higher than that in May. Specifically, the 1-year, 3-year, 5-year and 10-year changes rose: 8.46 bp, 3.32 bp, 2.78. Bp and 2.41 bp, the yield of 7-year government bonds fell slightly by 0.12 basis points. According to our calculations, the most recent treasury bills for the most expensive TD bond coupons (CTD vouchers) in the most recent month are: 110024, 140024 and 060019, corresponding to the CTD of the 10-year Treasury bond futures contract. The order of coupons is mainly 130011, 160006 and 130018. Regardless of liquidity or implied repo rate, 160006 is suitable as a CTD coupon for the 10-year bond contract. In the second half of this year, the downward pressure on the economy is still relatively large, but the vagueness is now showing signs of improvement. Although the inflationary pressure in the second half of the year is less than that in the first half of the year, the steady upward trend has already taken shape. Coupled with the pressure of RMB depreciation, the central bank’s loose space has been suppressed to some extent. The yield is difficult to go down and maintain the range volatility. National debt 110024 trend chart 9> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute National debt 160006 chart 10> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute Fourth, the funding side 1. Foreign exchange holdings fell into the normal state In May 2016, the central bank’s foreign exchange account fell by 53.102 billion yuan to 23.728 trillion yuan in a single month. This is the seventh consecutive month of decline in the central bank’s foreign exchange holdings since October last year. Despite the pressure of RMB depreciation, the decline in the central bank’s foreign exchange holdings has not expanded further than the one-month drop in April’s 54.395 billion yuan. At the end of last year, at the beginning of this year, there was a sharp drop in foreign exchange holdings. In January this year, the central bank’s calibre fell by 644.5 billion yuan, the second largest decline in history, after the drop of 708.2 billion yuan in December last year. Foreign exchange account Figure 11> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute According to the foreign exchange reserve, the cross-border flow of “hot money†shows that the cross-border outflow of “hot money†in January was 175.76 billion US dollars, and the outflow scale in February fell to 89.967 billion US dollars. The outflow scale in March further dropped 85.514 billion US dollars, and it flowed out in April. The scale was $979.60 billion, and in May it continued to rebound to $114.96 billion. From the big trend, China's weak economy, the expectation of tightening US monetary policy, and the rising uncertainty brought about by the economic and monetary policy differentiation between the United States and other countries have led to the continued outflow of funds. The RMB exchange rate is under pressure from depreciation. It is expected that capital outflows will continue to be more serious in the coming months. Hot money estimate Figure 12> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute 2. Credit growth continues to rise At the end of May 2016, the broad money (M2) balance was 146.17 trillion yuan, an increase of 11.8% year-on-year. The growth rate was 1.0 percentage point lower than the end of last month and 1.0 percentage point higher than the same period of last year. The narrow money (M1) balance was 42.43 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 23.7%, and the growth rate was 0.8 and 19.0 percentage points higher than the end of last month and the same period of last year. The growth rate of M2 dropped from 14% at the beginning of the year to 11.8%, while the growth rate of M1 increased from 2.9% in March 2015 to 23.7% in May 2016, which led to an increase in the scissors of M1-M2. In May, the value of scissors of M1-M2 was as high as 11.9%, which almost reached the historical peak. This also reflected the rise of liquidity preference and risk preference in the whole market, which will actually exert greater pressure on the future economic rebound. In the case of rising liquidity preferences, it is difficult for funds to be falsified, and funds are easily paralyzed in the financial system. In addition, in the economic downturn, lack of good investment opportunities, corporate funds from long-term deposits to short-term deposits, waiting to enter the capital market, rather than the production sector, which also led to a 3.9% year-on-year increase in private fixed-asset investment The growth rate hit a record low. In June last year, the credit expansion and the bailout funds entered the market in July, which raised the M2 balance. It is expected that the M2 year-on-year growth rate will decline slightly in the next few months. After the base effect disappears at the end of the year, the growth rate is expected to rebound. Year-on-year growth rate of money supply (2010.1—2016.5) Figure 13> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute At the end of May, the scale of social financing was 146.33 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 12.6%. Among them, the balance of RMB loans issued to the real economy was 98.92 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 14.0%. The cumulative increase in social financing scale from January to May was 8.10 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 1.15 trillion yuan. In the month of May, the scale of social financing increased by 659.9 billion yuan, which was 579.8 billion yuan less than the same period last year. Among them, entrusted loans increased by 156.6 billion yuan, an increase of 124.2 billion yuan year-on-year; trust loans increased by 12.1 billion yuan, an increase of 31.6 billion yuan; undiscounted bank acceptance bills decreased by 506.6 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 602.7 billion yuan; corporate bonds Net financing decreased by 39.7 billion yuan, down 210.7 billion yuan year-on-year; non-financial enterprises' domestic stock financing was 107.3 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 48.9 billion yuan. In terms of sub-items, both the rise in the table and the direct financing outside the table have fallen. The rebound in the table benefited from steady growth and continuous improvement in real estate sales, but the marginal role is gradually decreasing; the off-balance sheet is due to the new regulations on central bank bills regulation, the large amount of commercial bank bills business has been retired, and entrusted loans and trust loans have increased. The amount is slowing down. In addition, the bond market yields fluctuated and the corporate credit risk exposure was exposed, and the issuance of corporate bonds was also increased. At the end of May, the balance of domestic and foreign currency loans was 105.23 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 13.0%. At the end of the month, the balance of RMB loans was 100.10 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 14.4%. The growth rate was the same as that of the previous month, 0.4 percentage points higher than the same period of last year. In the month, RMB loans increased by 985.5 billion yuan, an increase of 88.7 billion yuan. In terms of sub-sectors, loans from the household sector increased by 575.9 billion yuan, of which short-term loans increased by 47.8 billion yuan, medium and long-term loans increased by 528.1 billion yuan, and loans from non-financial enterprises and institutions increased by 359.7 billion yuan, of which short-term loans decreased by 12.1 billion yuan. Medium and long-term loans increased by 182.5 billion yuan, bill financing increased by 156.4 billion yuan, and loans from non-banking financial institutions increased by 41.6 billion yuan. At the end of the month, the balance of foreign currency loans was 780.1 billion U.S. dollars, down 15.2% year-on-year. The foreign currency loans in the month decreased by 18.1 billion U.S. dollars. On the enterprise side, local debt swaps have led to loan repayments or the main reason for the increase in medium and long-term loans that are less than expected. The large increase in medium and long-term loans in the residential sector reflects the bank's preference for low-risk mortgage lending in the context of high real estate destocking and credit risk. In June, commercial banks faced MPA assessments, and it is expected that credit will decline in the later period. Under the pressure of economic downturn, credit risk may also rise. In order to maintain the GDP growth target and avoid systemic debt risks, monetary policy may continue to remain relatively loose in the short term. At the same time, however, the continued loose monetary policy will exacerbate the leverage risk of the real economy and may threaten the stability of the medium and long-term financial system. In addition, the active expansion of monetary policy will also lead to an increase in the pressure of RMB depreciation and capital outflows. It is expected that the government will fine-tune or moderate the monetary policy tone in the future, but considering the contradictions and conflicts between various policy objectives, future policies will face greater uncertainty. 3. The cost of funds remains stable Interbank bond repo rate Figure 14> Source: Wind Information, Ruida Futures Research Institute In the first half of the year, the liquidity was stable and neutral. Except for the central bank's RRR cut on February 29, the central bank's intention to eliminate the flooding of flooding in the first half of the year was further enhanced by open market operations and high-frequency structural monetary policy assistance. Targeted liquidity. The central bank did not cut the price of funds, but at the same time supplemented the liquidity demand by quantity. In terms of quantity, the central bank implements an open market rolling operation, plus a structured currency supplement. Compared with last year, the open market operation in the first half of the year was normalized. At the same time, the SLF and MLF were more flexible. Considering the market liquidity and the expectation of capital outflows, the overall situation of funds was relatively stable. In terms of capital costs, from January to May this year, SLF's overnight, 7-day and January interest rates were maintained at 2.75%, 3.25% and 3.60%, respectively, and MLF's 3M, 6M and 1Y were maintained at 2.75%, 2.85% and 3.00% respectively. The 7-day reverse repo rate has not changed since it was lowered from 2.35% to 2.25% on October 26 last year. In the second half of the year, the fund is expected to be stable. Under the MPA framework, the financial system is emphasized, and the probability of further marginal easing is lower. V. Policy Outlook and Investment Suggestions In terms of fundamentals, from the international perspective, the world economic recovery is fluctuating repeatedly. The Brexit makes the economic recovery in the euro zone more difficult, Japan’s economic growth is weak, and the monetary policy differentiation brought about by the accelerated growth of the US economy compared with other economies. It will inevitably have an impact on other major economies, including developed economies such as the European Union and Japan, as well as emerging economies. Therefore, the impact on China’s exports cannot be underestimated. Domestically, following the decline in economic growth in the first quarter, the economy in the second quarter ran smoothly, but the structural problems and deep-seated contradictions on the supply side were not completely resolved. There is still downward pressure on economic growth in the second half of the year. Industrial growth may fall further, and the possibility of new lows is also relatively high; high-frequency data shows that the country's real estate sales situation has gradually returned to a steady state, which also means that the growth rate of real estate investment will slow down in the second half of the year. Although infrastructure investment is expected to continue to grow rapidly in the short term, it is not enough to fully hedge the negative impact of the slowdown in real estate investment. Recently, the central and local governments have begun to investigate private investment and study corresponding measures to support private investment. In the second half of the year, the policy is expected to introduce more measures to actively guide investment growth. In the short term, the downward trend of private investment may be controlled, but the overall recovery It will take longer. In terms of consumption, the growth rate is expected to gradually slow down, with a year-on-year growth of around 9.5%. Compared with the first half of the year, external demand is not expected to improve significantly. There is still considerable pressure on imports and exports. The downside risks of economic growth cannot be underestimated. From the perspective of monetary policy, the overall framework is still the interest rate corridor to maintain liquidity price stability, open market operations and structured monetary policy tools to hedge liquidity and stabilize capital fluctuations. From the perspective of fiscal policy, under the situation of greater downward pressure on the economy, both the total demand management and the supply-side structural reforms need to play the role of active fiscal policy. The deficit rate is raised to 3% this year, the national debt net The circulation will reach 1.4 trillion, and the total issuance of local debt may be around 6.5-7.5 trillion. In the first half of the year, the local debt was issued to 3,755.5 billion, basically half of the amount has been completed, and the subsequent average monthly supply reached about 600-700 billion. In view of the impact of comprehensive monetary policy and fiscal policy, inflation expectations are superimposed on the pressure of RMB depreciation, the monetary policy operation space is further reduced, the central bank's monetary policy is prudent and cautious, coupled with the pressure on the supply of interest rate bonds, the short-term yield is stable and long. The downside of bond yields is limited. It is expected that the yields of five bonds and ten bonds will fluctuate between 2.30-2.70% and 2.80-3.10% in the second half of the year, and the debt operation will be dominated by shocks. The second part of the operational strategy 1. Intraday and short-term For short-term trading, the impact is relatively direct on the inter-bank market funds and interest rate bond market trading conditions and sentiment, these factors can basically be reflected in the short-term market changes. Therefore, short-term trading can directly refer to the technical form. Operation can refer to the 15-minute K-line cycle, with the 45-day moving average as the long-short reference. 2, the midline strategy The fundamental factors have weakened the impact on the bond market, the central bank's policy is stable, and the supply pressure is still large; with the supply-side reform, the long-term bond yields are difficult to change, and the range fluctuations are maintained. Strategy on the band operation, rallies short, buy on dips, profit and loss ratio of at least 3:1 is appropriate. TF1609 recommends an operating range of 99.900-101.200; T1609 suggests an operating range of 98.800-100.600. 3, cross-species arbitrage Judging from the price difference between the five bonds and the ten bonds in the most recent month, the price gap above 2.00 can be involved in the empty TF1609 multi-T1609 strategy, stop loss 2.2, target 1.20; the price difference below 0.6 can involve multiple TF1609 empty T1609 strategy, stop loss 0.35 , goal 1.5. Ruida Futures Research Institute Jersey Fabric,Cotton Jersey Fabric,Jersey Knit Fabric,Single Jersey Fabric Suzhou Zhiqin Textile CO.LTD , https://www.zhiqintextile.com
Client